Top Companies that Build Physical Product Prototypes of Your Idea

Prototyping is essential for visualising product ideas, gathering user feedback, and making design iterations to reduce costs and improve market fit.
Table of Contents
Choosing the right prototyping company is crucial, as different types offer varying techniques and expertise suited for specific stages. These companies cater to diverse industries, ensuring tailored solutions for various fields such as aerospace, telecommunications, and medical industries. The range of services a company offers can include support throughout the product lifecycle, from initial design to prototyping and production.
Engaging the target market during the prototyping process enhances customer satisfaction, informs design decisions, and prepares for launches.
Key Takeaways
- Prototyping is essential for visualising product ideas, gathering user feedback, and making design iterations to reduce costs and improve market fit.
- Choosing the right prototyping company is crucial, as different types offer varying techniques and expertise suited for specific product development stages.
- Engaging the target market during the prototyping process enhances customer satisfaction, informs design decisions, and prepares for successful product launches.
Understanding Physical Product Prototypes
A prototype is a tangible sample or model of a product idea, acting as the first step in transforming a concept into reality. The creation of prototypes involves a blend of craft, science, and technology, allowing designers and engineers to explore different design options and make informed decisions early in the development process. This process helps visualise and test user interactions, ultimately leading to more user-friendly final products.
Creating physical prototypes offers numerous benefits. Prototypes allow teams to observe the real size, material behaviour, feel, and colour of the product, which is crucial for gathering user feedback and making design iterations. Additionally, feedback obtained from physical prototypes can significantly reduce the likelihood of costly design changes later on, making the development process more efficient and cost-effective. Prototypes also allow teams to refine designs by testing and making necessary adjustments before mass production. Prototyping also plays a key role in assessing market viability and customer response before committing to mass production.
Prototypes serve multiple purposes, such as assessing functions, gathering feedback, and visualising the final product. Identifying and resolving issues before full-scale production streamlines the manufacturing process, improves the performance and appearance of the invention, and enhances market fit. Ultimately, physical prototypes bridge the gap between concept and reality, making it easier to communicate ideas to stakeholders and fostering better collaboration among team members, including the development of a high-quality prototype that ensures reliable and efficient prototypes to enhance product development.
Types of Prototyping Companies

When it comes to turning your product idea into a physical prototype, the type of prototyping company you choose plays a crucial role. Different companies offer various services, including 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection moulding, each catering to specific needs and stages of the product development process. These companies cover a broad spectrum of disciplines, from materials sciences to functional prototyping and rapid prototyping techniques. These companies boast extensive manufacturing capabilities, offering a range of advanced production methods to meet various industry needs. Understanding the types of prototyping companies can help you select the right partner to bring your concept to life. Additionally, some companies specialise in low-volume manufacturing, efficiently producing small quantities of parts or prototypes to provide customised solutions before mass production.
Prototyping companies can be categorised into three main types: rapid prototyping services, machine shops, and manufacturers. Each type has unique capabilities and focuses, making them suitable for different stages of the prototyping process. In the following subsections, we’ll delve into the specifics of each category, highlighting their strengths and how they contribute to the creation of physical prototypes.
Rapid Prototyping Services
Rapid prototyping services are designed to quickly produce and iterate on physical models, allowing product developers to test ideas and developments early in the process. This approach minimises risks and mistakes, providing a cost-effective way to explore different design options and gather valuable feedback. Rapid prototyping companies offer rapid prototyping services, including 3D printing and CNC machining, which facilitate fast alterations to designs and benefit both engineers and designers.
One of the primary advantages of rapid prototyping is the ability to quickly produce initial prototypes and refine them based on real-world feedback. The use of computer-aided design (CAD) and other advanced technologies enables swift adjustments and ensures that the prototypes meet the desired specifications. A CAD file provides detailed design specifications and measurements, which are crucial for accurate prototype creation. Rapid prototyping companies often provide individual approaches and collaborative support throughout the prototyping process, ensuring that various perspectives are considered.
However, it’s essential to choose a rapid prototyping company that offers comprehensive design and manufacturing support. Small 3D printing shops may lack professional product design engineers and the capability to handle multi-disciplinary projects involving hardware or electronics. Collaboration with designers, project managers, and engineering teams is crucial for effective prototype development and ensuring the final product meets all functional and aesthetic requirements.
Machine Shops
Machine shops play a critical role in creating precise and durable prototypes by utilizing advanced techniques such as CNC machining and laser cutting. These methods ensure high precision and repeatability, which is essential for producing prototypes that meet design specifications. Additionally, selective laser sintering is employed as an advanced rapid prototyping service to create high-quality and functional prototypes.
Machine shops excel in part manufacturing, providing comprehensive solutions for designing and producing components with high precision.
The expertise of mechanical engineers in machine shops allows for the creation of functional prototypes that can withstand rigorous testing and evaluation, making them ideal for the later stages of the prototyping process.
Manufacturers
Manufacturers typically focus on high volume orders, which can impact their willingness to create prototypes. Their primary interest lies in producing large quantities quickly, making them more suited for mass production rather than the initial prototyping stage. However, some manufacturers do engage in the prototyping process, especially if there’s a potential for substantial future orders. Reducing lead times for efficient delivery of prototypes is crucial, as it can significantly impact the product development process and enhance the ability to bring products to market more quickly. Some manufacturers also offer low volume production services, catering to clients who need smaller production runs before committing to large-scale manufacturing. It’s important to note that working with manufacturers can involve risks, such as losing intellectual property rights.
While some manufacturing companies may not build prototypes due to lower profit margins and higher risks, others may require a Letter of Intent (LOI) as a commitment during the prototyping process. This ensures that the investment in creating the prototype is justified by the potential for large-scale production.
Understanding the dynamics of working with manufacturers can help you make informed decisions during the prototyping stage and prepare for eventual mass production.
Choosing the Right Prototyping Company

Selecting the right prototyping company is a critical decision in the product development process. Understanding the purpose of your prototype—whether for testing, demonstrating product feasibility, or gathering user feedback—is crucial. Key factors to consider include the complexity of your product, the resources available within the prototyping company, and the development roadmap you envision. A company with a strong reputation can provide the expertise and reliability needed to bring your product idea to life.
A prototyping company with excellent project management expertise can significantly influence the outcome of your product development process. The integration of cutting-edge technology, such as 3D printing and advanced manufacturing methods, ensures effective prototype development by enhancing speed and precision. The company must understand the necessary specifications and maintain effective quality control systems to ensure the integrity of your prototype. Focusing on user experiences during the prototyping process ensures that the final product meets user expectations and achieves its intended goals.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a prototyping company that aligns with your goals and can bring your product idea to life efficiently and effectively.
Leading Prototyping Companies
Industry certifications are a key indicator of the quality of work and operations within prototyping companies, aligning their processes with industry standards. Among the top prototyping companies, Bluefrog Design stands out for its technical expertise and design skills. Each leading prototyping company specialises in different aspects of rapid prototyping, ensuring high-quality prototypes tailored to client specifications.
These companies serve various industries, including automotive, aerospace, healthcare, consumer electronics, and consumer goods, showcasing their versatility and expertise.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Bluefrog Design is renowned for producing a wide range of prototypes, from small handheld models to large-scale ergonomic rigs. Their appearance models play a critical role in testing products with the target audience and gathering feedback, ensuring that the final digital products meet both aesthetic and functional requirements, thereby enhancing the overall user experience. Ergonomic models are designed to change and test different aspects of the product with various user groups, optimising features such as handles, controls, and displays.
Clients recognize Bluefrog Design’s technical expertise and design skills as significant strengths. Their model-making process is essential for refining design features, ensuring that products meet both aesthetic and functional requirements. Bluefrog Design UK specializes in prototyping solutions for medical devices, laboratory equipment, and surgical instruments, showcasing their ability to handle complex and specialized projects.
One notable example of Bluefrog Design’s work is their involvement with Zephyr®, for which they provided concept designs that showcased various potential solutions. Their use of rapid prototyping processes such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and sheet metal fabrication enables them to produce high-quality prototypes efficiently.
Steps to Create a Physical Prototype
Creating a physical prototype involves a series of steps that transform sketches into tangible products. The process starts with the purpose of the prototype, guiding the development from concept design to building the first prototype and testing and refinement, often utilizing 3D printed technologies to highlight the significance of rapid prototyping. The initial design phase is crucial for setting the foundation of the prototype, guiding the development from concept to tangible product.
Each step is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications and is ready for mass production. Building rough or mockup prototypes helps refine designs by testing core functionality and making necessary adjustments early in the process.
Concept Design
The concept design phase is the first step in the prototyping process, where multiple concepts are explored to understand different user interactions and product ideas. A visual prototyping brief should include essential features, functionality, and potential materials, serving as a roadmap for the design process. The simplest way to create a digital prototype is through pen and paper sketches, which can then be translated into 3D CAD modeling for more detailed design and modeling of the product idea. Prototyping tools specifically designed for mobile apps can enhance this process, ensuring that mobile apps are visually appealing, functional, and user-friendly.
Building rough or mockup prototypes, also known as Proof of Concept Rigs, is essential for proving the concept and ensuring core functionality. These prototypes help determine if a theoretical concept can be realized and facilitate early testing.
A looks-like prototype can also be useful for initial target audience surveys or market research, providing valuable insights into potential design flaws and user preferences.
Building the First Prototype
Building the first prototype involves choosing the right methods and materials to create a working prototype. Common processes include 3D printing, CNC machining, laser cutting, resin casting, and pre-production tooling. These methods allow for quick iterations between design, prototype, and testing, enabling continuous improvement based on real-world feedback. CAD files play a crucial role in the prototyping process, providing detailed specifications needed for accurate prototype creation. Materials commonly used in 3D printing for prototypes include plastic, rubber, and nylon, which offer versatility and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, vacuum casting is another effective method for producing high-quality prototypes efficiently and cost-effectively.
DIY approaches can also be a viable option for building the first prototype, especially for simple designs or when cost is a significant concern. Materials like paper, cardboard, and plastic can be used to create cost-effective prototypes, allowing for initial testing and refinement. The use of CAD software in rapid prototyping enables swift adjustments and refinements, ensuring that the prototype meets the desired specifications. The iterative process of building and testing prototypes helps refine designs, ensuring that the final product meets all desired specifications.
The first prototype often results in a rougher finish and typically lower performance characteristics than the final product, but it is a crucial step in the development process. By identifying and addressing design issues early on, you can prepare for mass production with confidence.
Testing and Refinement
The iterative process of testing and refining a prototype continues until user needs are adequately met. Testing prototype products allows teams to refine designs by identifying and addressing any issues early in the development process, showcasing the design and manufacturing capabilities of companies. Testing prototypes involves gathering user feedback to identify areas for improvement and incorporating usability testing to uncover real-world issues. This process helps detect design flaws early, leading to less costly revisions during the development cycle.
A/B testing can provide insights into user preferences, helping to refine design choices based on performance data. Incorporating user experiences into the testing phase ensures that the final product meets user needs and expectations. Iterative testing is crucial for ensuring that the prototype meets all functional requirements and is ready for full-scale production.
Cost Considerations for Prototyping
Cost considerations are a critical aspect of the prototyping process. The cost structure for prototyping services can vary significantly based on the chosen manufacturing technique and the complexity of the design. Different materials can lead to varying costs, with special materials like PEEK being considerably pricier than common options like ABS. Additionally, the involvement of electronics, mechanics, software, or labour-intensive assembly can significantly increase the cost of a product prototype. Total revenue generated by companies can reflect their ability to invest in high-quality prototyping services, highlighting their financial performance within the industry.
Focusing on necessary features and using cost-effective materials can help reduce production costs during the prototyping process. Minimising prototype costs requires focusing on necessary features only and avoiding the creation of multiple prototypes unless absolutely necessary. Prioritizing electrical work over mechanical, starting with a scaled-down model, using cheaper materials initially, and automating with machinery are effective strategies to reduce costs. Despite the higher initial costs, creating a prototype can save money in the long run by preventing substantial investments needed for corrections later.
Prototypes typically cost more than full-scale production due to the lack of volume discounts and the custom approaches required. However, rapid prototyping allows teams to create cost-effective prototypes, enabling efficient testing of multiple designs and ensuring the final product meets all functional and performance criteria.
Protecting Your Intellectual Property
Protecting your intellectual property (IP) is crucial during the prototyping process. If you don’t legally protect your product idea, suppliers might take your product idea and produce it themselves. Consulting an IP lawyer for trademarks and patents ensures that your product design is legally protected before you begin prototyping. Filing a provisional patent application and documenting your invention can secure patent protection and establish ownership of the idea.
Engaging Your Target Market
Engaging your target market is an essential part of the prototyping process. It starts with market research to understand user needs and competition, which helps shape the design and development of your product. Utilising prototyping tools in web design for websites and applications can streamline the design process by offering integrations, UI components, and templates that enhance efficiency. Gathering feedback on prototypes reveals design improvements, increasing product appreciation and satisfaction. This feedback should be analyzed carefully to assess its impact across the entire customer base.
Engaging with the target market early in the development process helps ensure that the final product meets user experiences and expectations.
Engaging potential users during product development turns them into loyal customers who see you as a caring individual. Strategies like using social media, developing a website, and creating a newsletter can build an audience before the product launch.
Additionally, writing blogs about the product can attract early adopters while addressing related issues. By focusing on marketing and commercialization strategies during prototype development, you can prepare for audience engagement and ensure a successful product launch.
Real-World Examples of Successful Prototyping
Many successful products have gone through extensive prototyping stages, refining designs and validating ideas before reaching the market. For instance, the development of the Pebble Smartwatch involved creating 20 different prototypes, which helped refine its features before launch. Similarly, Airbnb’s founders built a prototype of their product to test the market’s interest, leading to significant improvements based on user feedback.
The Nest Learning Thermostat went through over 60 prototypes, allowing the team to focus on usability and user interface. Apple reportedly created around 100 different versions of the iPhone before finalising the design, showcasing the importance of extensive prototyping in developing a successful product.
These real-world examples highlight how prototyping can lead to innovative and user-friendly products that resonate with the market.
Leveraging Rapid Prototyping Techniques
Rapid prototyping techniques have revolutionised the product development process by enabling quick production of physical parts from 3D designs. Common technologies utilised in rapid prototyping include CAD, 3D printing, water jet or laser cutting, CNC machining, and software development. These technologies allow for fast iterations between digital designs and physical prototypes, significantly reducing time to market and enhancing the overall product development process. Rapid prototyping techniques allow for quick iterations, helping teams refine designs and ensure that the final product meets all desired specifications.
Common technologies utilised in rapid prototyping include:
- CAD
- 3D printing
- Water jet or laser cutting
- CNC machining
- Software development
These technologies allow for fast iterations between digital designs and physical prototypes, significantly reducing time to market and enhancing the overall product development process.
Top prototyping firms often employ specialised technologies to enhance efficiency and quality. The advancements in rapid prototyping techniques have made the prototyping process faster and reduced the number of iterations needed to achieve the final design. By leveraging these techniques, product developers can build prototypes quickly, test multiple designs, and make necessary adjustments to ensure the final product meets all functional and aesthetic requirements. Incorporating user experiences into the prototyping process helps create products that resonate with the market and meet user needs.
Preparing for Mass Production
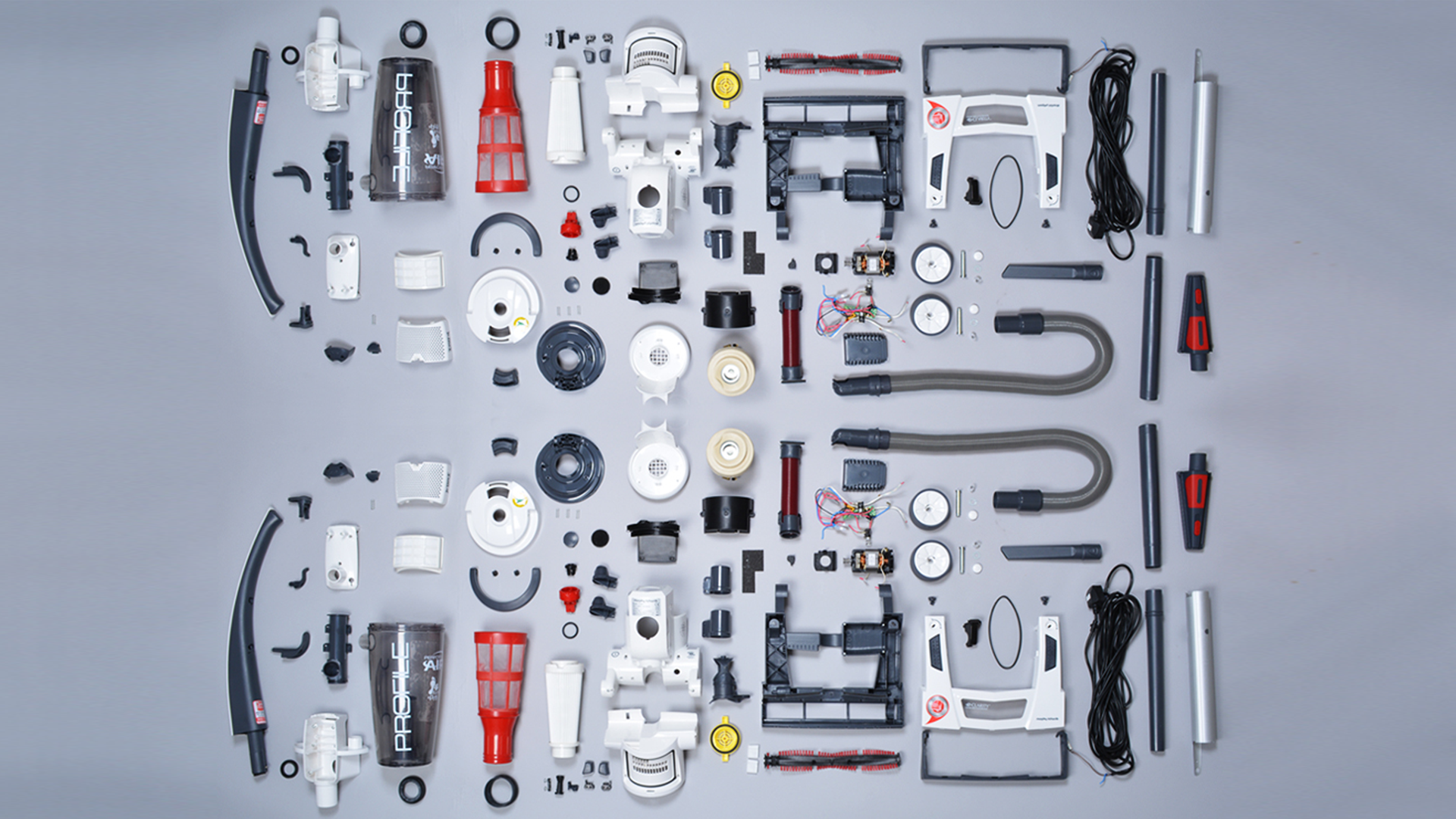
Preparing for mass production is a crucial step after the prototyping stage. Fine-tuning the design, preparing for production, and conducting market surveys are essential to ensure the product is ready for large-scale manufacturing. This comprehensive approach to additive manufacturing, where one manufactures functional prototypes and final parts, ensures that the final product meets all desired specifications. Cost-efficient production and assembly require moulds (tooling) and jigs, with the initial samples made after tooling referred to as first articles (samples). These samples help identify any necessary modifications to the moulds, such as adjusting the size of parts or adding/removing design features.
Post-production evaluation should focus on key performance metrics such as efficiency, quality, and overall satisfaction from stakeholders. Incorporating user experiences into the preparation process helps create products that resonate with the market and meet user needs. Addressing these aspects ensures that the final product meets the desired standards and is ready for full-scale production.
Sandblasting can provide a rougher finish to plastic injection moulds, affecting the quality of the final product. Preparing thoroughly for mass production ensures a smooth transition from prototype to finished product
Trends in Prototyping
The rapid prototyping industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging to improve the design and development process. Here are some of the current trends in prototyping:
- Increased Adoption of 3D Printing: 3D printing is becoming increasingly popular in the prototyping industry, allowing for the rapid creation of complex geometries and functional prototypes. This technology enables designers to quickly produce high-quality prototypes that closely resemble the final product, facilitating faster iterations and reducing production costs.
- Growing Demand for On-Demand Manufacturing Services: On-demand manufacturing services are becoming more popular, allowing companies to quickly produce small batches of parts without the need for large-scale production. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for startups and small businesses, enabling them to test and refine their designs before committing to mass production.
- Rise of Digital Prototyping: Digital prototyping is becoming more prevalent, allowing designers to create interactive and immersive prototypes without the need for physical models. Tools like Adobe XD and Figma enable the creation of clickable prototypes that simulate real-world user interactions, providing valuable insights during the development process, especially in mobile development where app prototyping tools cater to unique requirements.
- Increased Focus on Sustainability: There is a growing focus on sustainability in the prototyping industry, with companies looking for ways to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact. This includes using eco-friendly materials and adopting manufacturing processes that are more energy-efficient and produce less waste.
- Advances in CNC Machining: CNC machining is becoming more advanced, allowing for the rapid creation of complex parts with high precision and accuracy. This technology is essential for creating functional prototypes that require tight tolerances and high-quality finishes, making it a cornerstone of modern prototyping services.
- Growing Importance of User Feedback: User feedback is becoming increasingly important in the prototyping process, with companies using feedback to refine and improve their designs. Engaging with the target market early in the development process helps ensure that the final product meets user needs and expectations, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Increased Use of Prototyping Tools: Prototyping tools, such as Adobe XD and Figma, are becoming more popular, allowing designers to create interactive and immersive prototypes quickly and easily. These tools streamline the prototyping process, enabling rapid iterations and facilitating better collaboration among team members.
- Growing Demand for Rapid Prototyping Services: Rapid prototyping services are becoming more popular, allowing companies to quickly create functional prototypes and test their designs. This approach minimizes risks and mistakes, providing a cost-effective way to explore different design options and gather valuable feedback.
- Increased Focus on Collaboration: Collaboration is becoming more important in the prototyping process, with companies using tools and techniques to facilitate communication and collaboration between designers, engineers, and stakeholders. This collaborative approach ensures that all perspectives are considered, leading to more innovative and effective product designs.
- Advances in Virtual and Augmented Reality: Virtual and augmented reality are becoming more advanced, allowing designers to create immersive and interactive prototypes that simulate real-world experiences. These technologies provide a powerful way to visualize and test product designs, enhancing the overall development process.
These trends are shaping the future of prototyping, enabling companies to create innovative and effective products that meet the needs of their customers. By staying updated with these trends, businesses can leverage cutting-edge technologies and techniques to streamline their prototyping process and bring their product ideas to life more efficiently.
Prototype Design and Development
Prototype design and development is a crucial stage in the product development process. It involves creating a preliminary version of a product or system to test its feasibility, functionality, and performance. The goal of prototype design and development is to create a functional prototype that can be used to validate assumptions, gather feedback, and refine the design before moving into mass production.
In the context of rapid prototyping, prototype design and development involves using advanced technologies such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection moulding to create high-quality prototypes quickly and efficiently. This allows companies to test and refine their products in a shorter amount of time, reducing the risk of errors and improving the overall quality of the final product. By leveraging these cutting-edge technologies, companies can produce prototypes that closely resemble the final product, ensuring that all design specifications are met and that the product is ready for mass production.
The development process typically starts with a detailed design phase, where the initial concept is translated into a digital model using CAD software. This model is then used to create a physical prototype through various manufacturing processes. Throughout this process, continuous testing and refinement are essential to ensure that the prototype meets all functional and aesthetic requirements. By focusing on creating high-quality prototypes, companies can streamline the development process and bring their product ideas to life more efficiently.
Rapid Prototyping in the United Kingdom
Rapid prototyping is a growing industry in the United Kingdom, with many companies offering rapid prototyping services to clients across various industries. The UK is home to a number of top rapid prototyping companies, including Bluefrog Design. These companies are known for their expertise in creating high-quality prototypes using advanced technologies and innovative manufacturing processes.
These companies offer a range of rapid prototyping services, including 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection molding. They also provide expertise in design for manufacturability, material selection, and post-processing operations. By leveraging these services, companies can quickly produce functional prototypes that meet all design specifications and are ready for further testing and refinement.
The UK’s rapid prototyping industry is known for its strong focus on innovation and quality. Companies in this sector are continually adopting new technologies and techniques to improve the prototyping process and deliver better results for their clients. Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, healthcare, or consumer electronics industry, the UK’s rapid prototyping companies have the expertise and capabilities to help you bring your product ideas to life.
Working with a Rapid Prototyping Company
Working with a rapid prototyping company can be a highly effective way to bring your product ideas to life. These companies offer a range of services, from design and development to manufacturing and testing. By partnering with a rapid prototyping company, you can leverage their expertise and capabilities to create high-quality prototypes that meet all your design specifications.
When selecting a rapid prototyping company, it’s essential to consider factors such as their expertise, capabilities, and track record. Look for companies that have a strong reputation for delivering high-quality prototypes on time and within budget. A company with a proven track record can provide the reliability and expertise needed to ensure the success of your project.
You should also look for companies that offer a comprehensive range of services, including design for manufacturability, material selection, and post-processing operations. A dedicated team of experts who can provide valuable insights and support throughout the prototyping process is crucial. This collaborative approach ensures that all perspectives are considered, leading to more innovative and effective product designs.
In addition, it’s important to ensure that the company you choose offers flexible pricing options and can accommodate your specific needs and requirements. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a rapid prototyping company that aligns with your goals and can help you bring your product ideas to life efficiently and effectively.
Summary
Prototyping is a vital part of the product development process, offering numerous benefits such as improved design, user feedback, and cost savings. Choosing the right prototyping company, understanding the steps involved, and protecting your intellectual property are crucial for success. By engaging your target market and leveraging rapid prototyping techniques, you can create innovative and user-friendly products ready for mass production. Embrace the prototyping journey, and turn your product ideas into reality.
View more of our Product Development Services
If you would like to hear more on how we can improve the quality of your products or help with your product development, please contact Bluefrog Design at [email protected]
FAQ’s
What is an example of a physical prototype?
A physical prototype can be a model car made from cardboard or foam core board that mimics the features of real cars. This tangible representation allows for testing and refinement of design concepts.
How to get a physical prototype made?
To get a physical prototype made, start by sketching your design and consider using digital tools or 3D printing for a tangible model. Alternatively, you can build a minimum viable product or outsource the prototype creation to experts for assistance.
What is the main purpose of creating a prototype?
The main purpose of creating a prototype is to identify and resolve issues before full-scale production, which ultimately saves time and money while enhancing product design and functionality.
How do rapid prototyping techniques benefit product development?
Rapid prototyping techniques significantly enhance product development by facilitating quick production and iterative testing of models, which streamlines design refinement and accelerates time to market. This approach ensures a more efficient and effective development process.
What factors should I consider when choosing a prototyping company?
When choosing a prototyping company, prioritise the purpose of the prototype, the complexity of your product, available resources, and the company’s project management capabilities to ensure they can meet your specifications effectively.
Ready to get started on a project?
Socials



