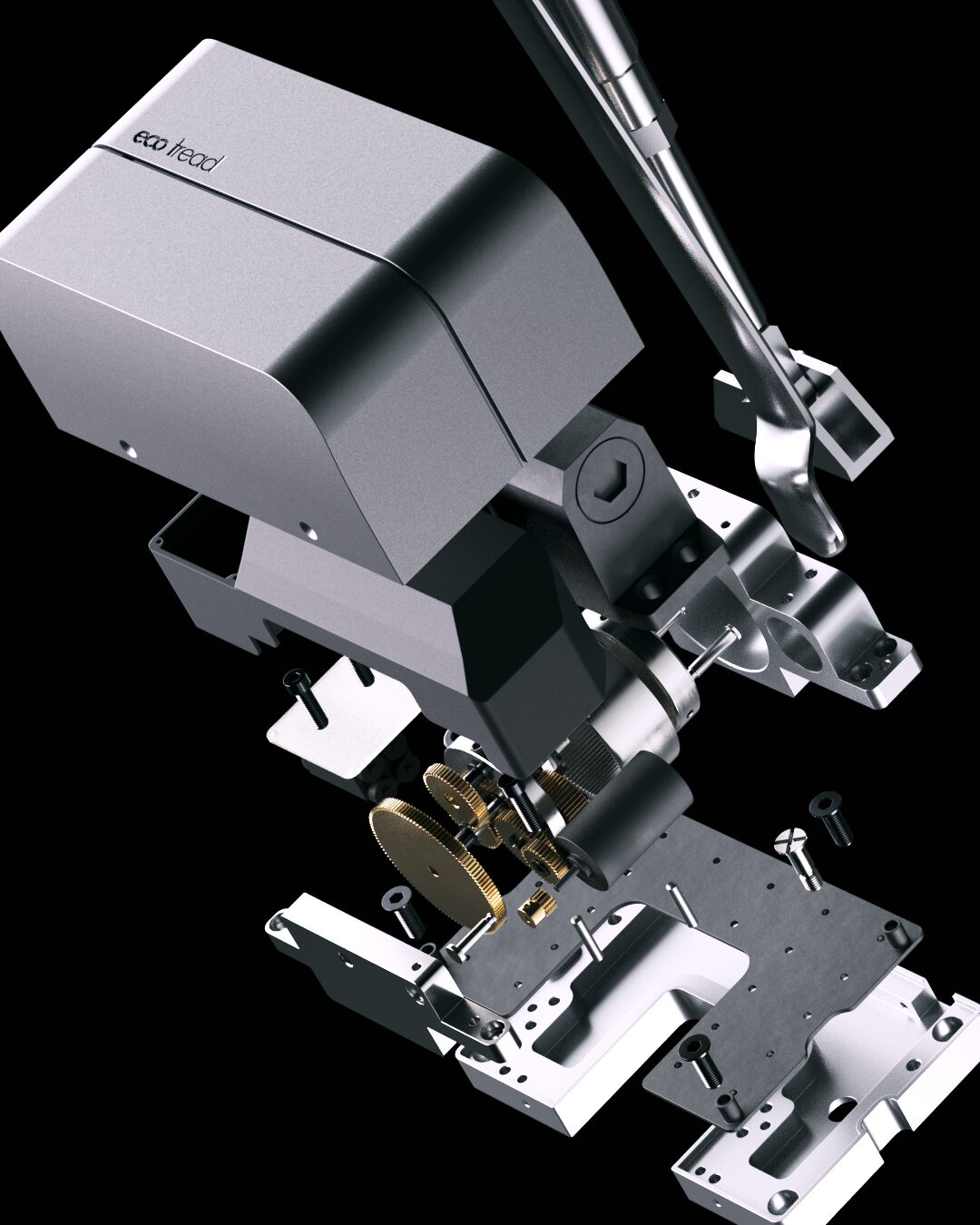
What is 3D CAD? – Computer Aided Design and Its Uses
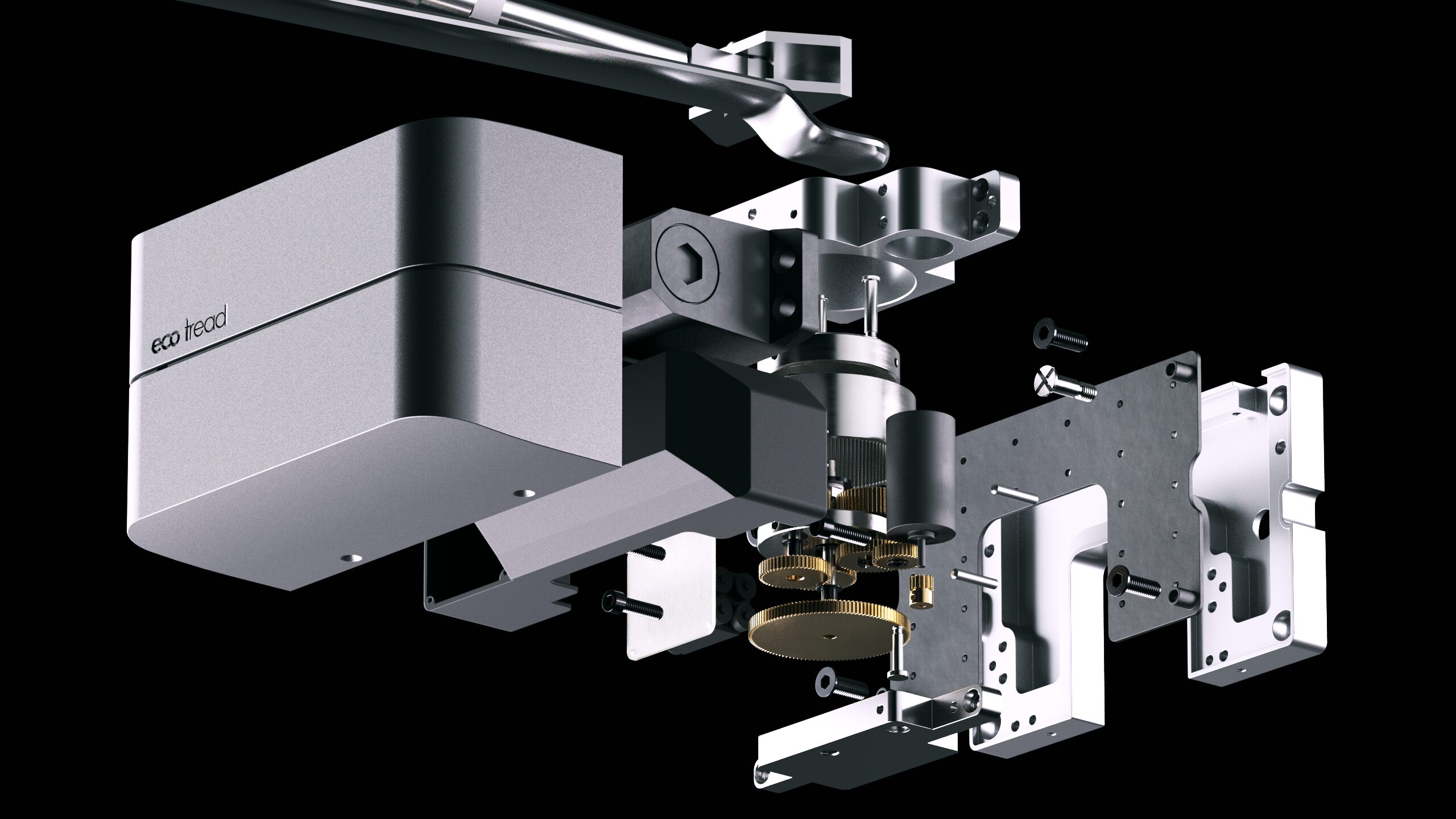
What is CAD and What is Computer Aided Design
What is computer-aided design? Computer-aided design (CAD) is a must-have in today’s engineering, architecture and product design. CAD certificate courses offered by educational institutions are a must for students in engineering and architecture. CAD computer-aided design uses computer systems to help designers modify, analyse and optimise designs, to improve the quality and productivity of the database.
Table of Contents
History of CAD
CAD has evolved from simple electronic drafting to complex systems that can do complex engineering calculations and extensive automation, a lot of technological advancements over the years. CAD programs have replaced manual drafting in various industries. This evolution has given birth to different types of CAD programs, each designed for a specific industry and design requirements. Most CAD software doesn’t require special hardware for basic operations but advanced features may require a modern graphics card and lots of RAM.
Functions of CAD in Design and Manufacturing
In industries where precision and speed are key, CAD is a must-have. A CAD system speeds up the design process, and allows for quick modifications and control over the final output, important in both design and manufacturing stages.
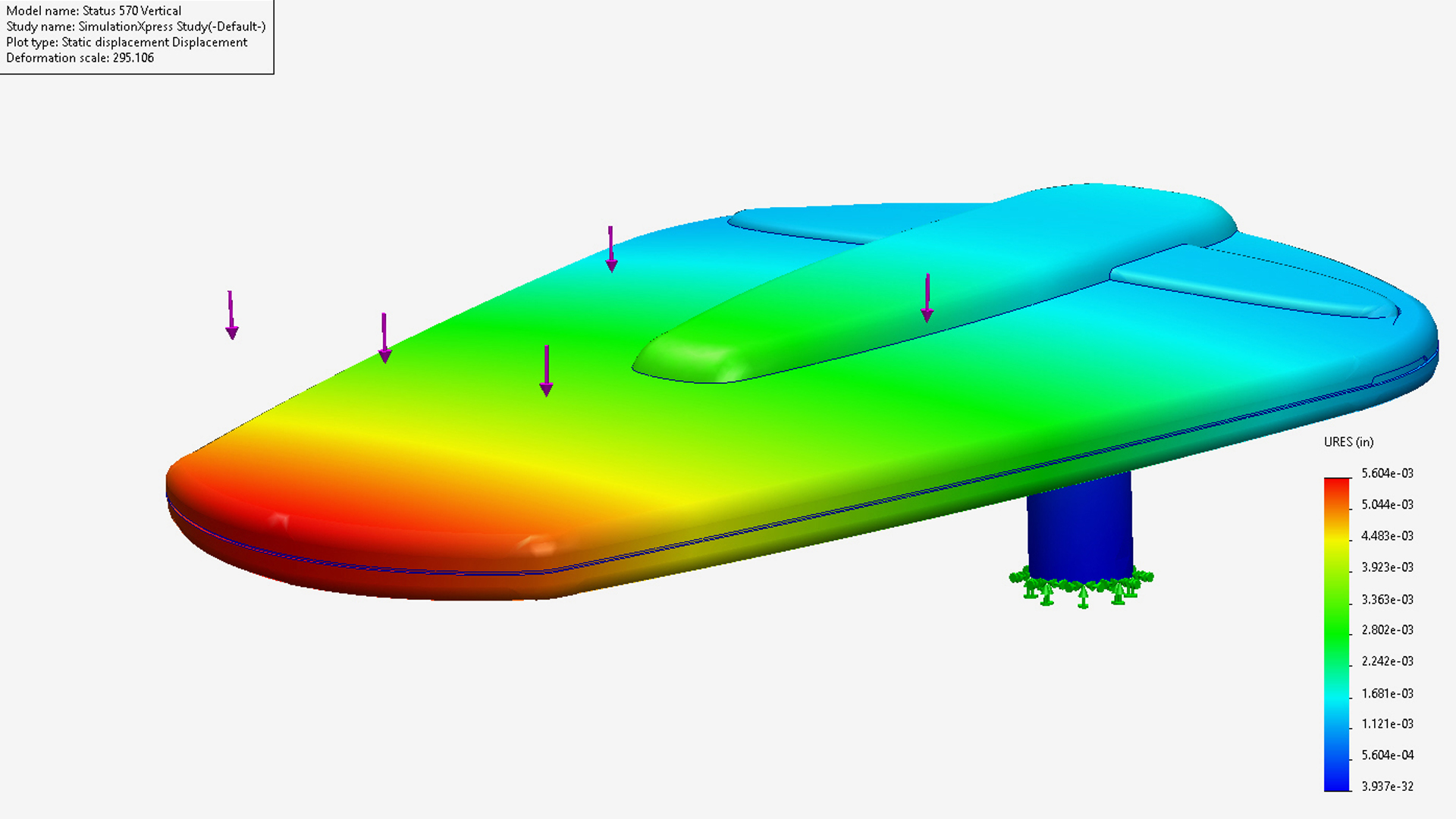
Types of CAD Systems
- 2D CAD: Used for flat drawings and layouts, 2D CAD allows adjustments and scaling on project drafts.
- 3D CAD: Allows the creation of volumetric and detailed models using CAD tools, important for complex designs and advanced engineering projects.
- Freeform CAD: Acts as a bridge between 2D and 3D, and allows designers to work with shapes that have depth but not fully 3D. The availability of different software packages makes these designs more flexible and efficient.
What is Surface Modelling?
Surface model allows designers to work with complex curved surfaces, often used in the automotive and aerospace industry where aerodynamics and detailed aesthetics are required.
What is Solid Modelling?
Solid modelling is a more advanced form of CAD that represents the volume of the object, not just its shape and surface. It’s used for simulations and functional analysis.
What is Parametric Modelling?
Parametric modelling uses parameters to define a system’s dimensions and properties, and allows quick modifications and iterations in the design process.
What is Generative Design?
Generative design uses algorithms to generate design options based on constraints and desired outcomes, and optimises material usage and functionality.
CAD Software and Their Uses
Talking about popular CAD software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks and Fusion 360, users can create, design and collaborate from any computer or mobile device, showing flexibility and convenience. These are computer software that boosts productivity in the design and manufacturing process and allows precise and efficient creation, modification and optimisation of designs across industries. This section explains their uses across different industries, features and benefits.
CAD Across Industries
- Architecture and Interior Design: For drafting detailed buildings and interior spaces. Interior designers use CAD software to create detailed layouts and visualise spaces in 3D, to communicate with architects, interior designers and clients for efficient planning and execution of interior design details.
- Engineering and Product Design: For detailed technical drawings and material specifications. CAD software is very relevant in mechanical engineering where both basic and advanced programs are used. While basic CAD can be learned fast, those for complex fields like mechanical engineering may require extensive training.
- Manufacturing and Production: For laying out manufacturing processes and planning production cycles.
- Automotive and Aerospace: From conceptual sketch to detailed assembly of vehicles and aircraft.
- Fashion and Textile Design: For pattern making and tailoring designs to specific fabric behaviour.
- Dental and Medical: For designing precise medical implants and devices.
CAD vs Traditional Methods
Efficiency, accuracy and productivity of CAD over manual drafting and sketching, how it translates to cost saving and better output. CAD files help in the design process by providing an accurate representation of the object’s dimensions and attributes, easier to share, edit and collaborate.
View more of our Product Development Services
If you would like to hear more on how we can improve the quality of your products or help with your product development, please contact Bluefrog Design at mail@bluefrogdesign.co.uk
FAQ’s on What Product Designers Do?
What skills do product designers in an industrial design consultancy need?
Product designers need a mix of creative and technical skills including CAD skills, material knowledge and an eye for aesthetics and market trends.
How do product designers in consultancies work with others?
They often work with engineers, marketers and UX designers to ensure the product is feasible, meets market needs and is user centric.
What are the career prospects for product designers in industrial design firms?
Career prospects are good, working on many different projects across many industries and often leading to design management or specialisation in specific product types.
Ready to get started on a project?
Socials