A Comprehensive Guide to 3D Rapid Prototyping
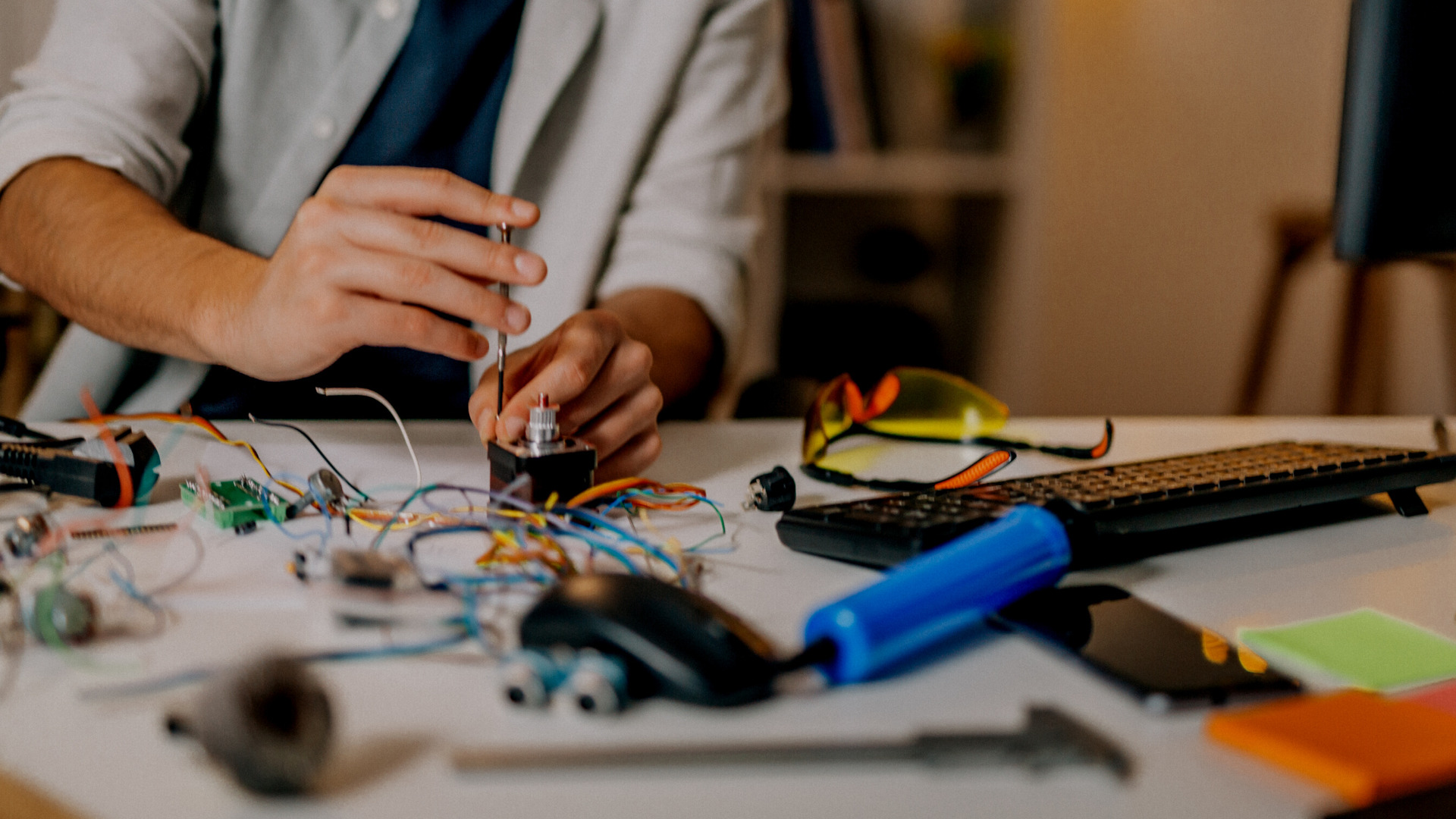
In the intricate journey of developing a product, 3D rapid prototyping stands out as a pivotal phase. The significance of product design prototyping is underscored by countless research and real-world scenarios. It not only streamlines the product development cycle but also economises resources and minimises risks before moving into full-scale manufacture.
Table of Contents

Understanding 3D Rapid Prototyping: The Basics
At its core, prototyping refers to creating a functional version of the product that has been designed, utilising materials that mirror those intended for final production. Such prototypes, termed as “functional prototypes”, serve to validate a design engineer’s efforts and help to facilitate comprehensive functional tests. In certain instances, these prototypes can also be employed for Compliance Testing and Certification by agencies such as UL, FCC, TUV, CE, and CSA. However, it’s essential to note that specific certifications might demand actual production parts instead of machined samples.
In a broader context, prototyping encompasses a series of validation checks during the development process. Whether it’s form studies to evaluate ergonomics, subsystem test builds for early function validation, or engineering prototypes for pre-production evaluation; prototyping is integral to ensuring the final product meets its intended objectives.
While the above sheds light on physical product prototyping, the concept is equally important to digital products like software applications and websites. Google’s “Design Sprints” exemplify rapid prototyping for digital products. This accelerated method involves problem identification, solution conceptualisation, prototyping, and testing – all within a span of approximately five days.
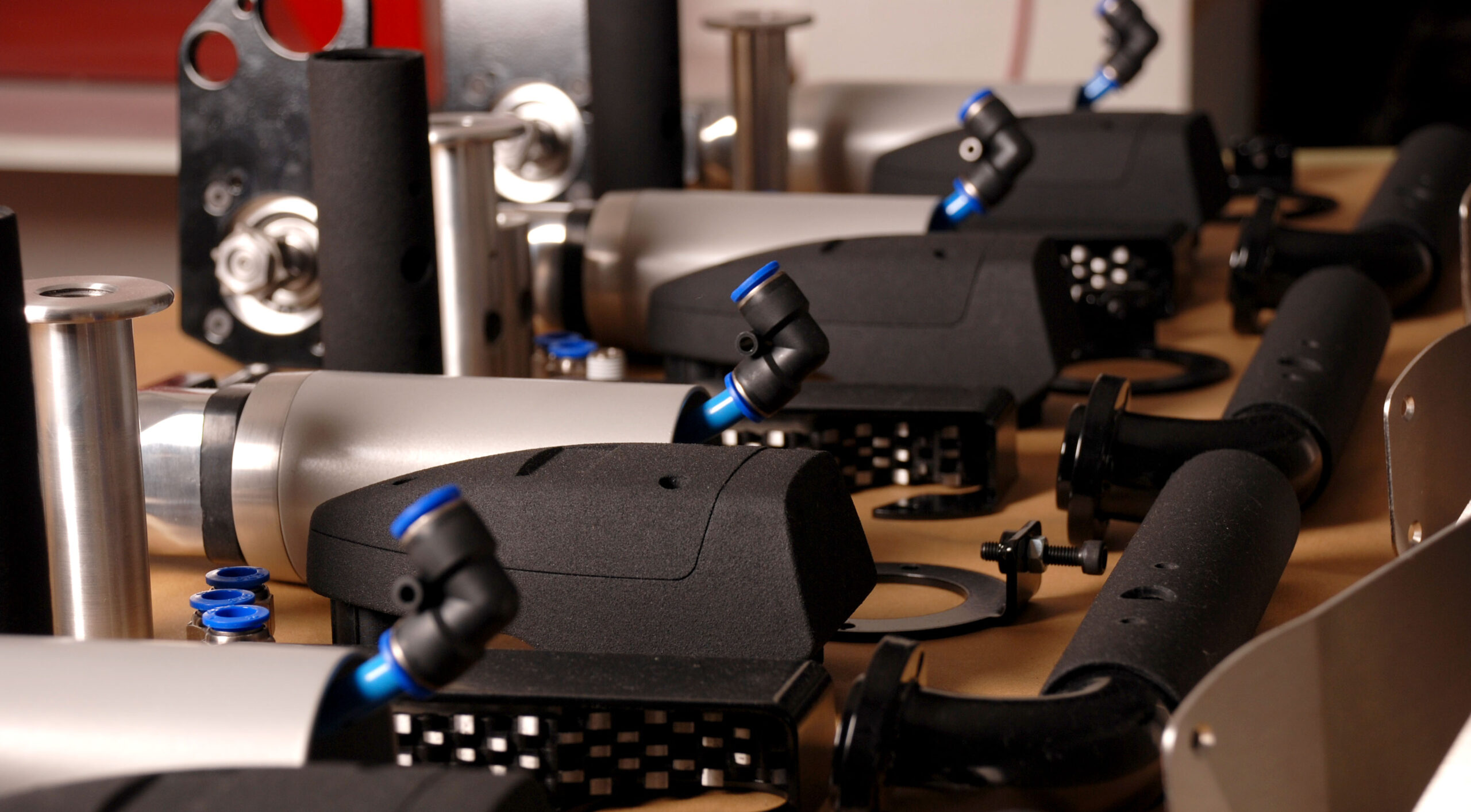

The 3D Rapid Prototyping Spectrum
- Sketch Models: Initial prototypes are imperative for tangible products to gauge their spatial feel and resolve ergonomic concerns. Especially with handheld or wearable products, these prototypes can offer crucial insights into aesthetics and user comfort. For instance, a glucose testing system prototype revealed the need for a size reduction to meet market expectations, based on global testing feedback.
- Appearance Models: Meticulously crafted appearance models stand as industry benchmarks for realism and precision, providing an unparalleled platform for product testing within your target demographic. Upon engaging with these models, prospective users offer invaluable insights that enable us to employ a sophisticated, knowledge-driven design approach. We ensure that every facet of the design, from colour palettes, finishes, and textures to materials and graphics, mirrors the finalised product. This commitment guarantees that user feedback is grounded in genuine, trustworthy interactions with the prototype, ensuring decisions made are based on authentic and reliable user responses.
- Proof of Concept Rigs: This category focuses on ensuring subsystem functionality at an early stage, minimising the risk of late-stage product failures. Sometimes, various methods to achieve a function need testing. These multi-purpose test units help validate different configurations and settings. For instance, medical surgical carts have been prototyped numerous times to ensure optimal display and control placements, vital for critical medical situations.
- Functional Prototypes: These prototypes are crafted from materials closely mirroring the final product. They serve to validate the 3D CAD engineering designs, ensuring that the end product aligns perfectly with the envisioned concept. For instance, when suggesting a specific material, the prototype will be made from the machine-grade version of that. The fidelity of these prototypes aids in early detection of potential pitfalls, ensuring smoother transitions to the production phase.
- Medical Prototypes: The crux of medical device development lies in swiftly bringing to market products that are not only clinically significant but also possess strong market appeal. Through our unparalleled medical prototyping solutions, we expedite design optimization, ensuring swift testing, approval, and verification pre-launch. Our experience in product design encompasses an array of projects, from medical devices and laboratory apparatus to drug delivery systems, surgical tools, diagnostics, and prosthetics. Leveraging cutting-edge in-house technologies, we craft medical prototypes poised to secure the most stringent regulatory approvals. We specialise in fabricating parts using biocompatible materials compliant with industry standards, harnessing techniques like 3D printing, CNC machining, and precision injection moulding.
- Electronic Prototypes: electronic components often emerge as the most capital-intensive and time-intensive elements. Therefore, it is imperative to validate the concept prior to incurring substantial development costs. Initiating with an electronic prototype serves to rigorously ascertain both performance and functionality, sidestepping protracted lead times and financial implications. Our team of expert electronic engineers craft advanced analog prototypes for swift assessments, adeptly pinpointing process mapping and logic discrepancies via versatile platforms like PLCs, Arduino development boards, or single-board PCs like the Raspberry Pi. We engineer prototypes that empower you to pioneer groundbreaking ideas and confidently channel investments into bespoke hardware tailored to your product’s unique demands.
In conclusion, 3D rapid prototyping offers invaluable insights into market reception, allowing for pre-production fine-tuning based on real-world feedback. It’s not just about validation but also about optimisation. By facilitating early error detection, prototyping ensures that the final product resonates with its target audience and meets operational benchmarks. Thus, for anyone embarking on a product development journey, remember the adage: prototype swiftly and frequently. Your product’s success might very well hinge on it.
Our Design Services
If you would like to hear more on how we can improve the quality of your products or help with your product development, please contact Bluefrog Design at mail@bluefrogdesign.co.uk
FAQ’s about 3D Rapid Prototyping
What is 3D rapid prototyping in product design?
3D rapid prototyping in product design is the process of creating a preliminary model or replica of a product to test and validate its functionality, aesthetics, and usability before final production. This model, or “prototype”, allows designers to identify potential flaws, gather user feedback, and make necessary refinements. By simulating the final product, prototyping reduces risks, saves costs, and ensures a better end result in the production phase.
What is the best 3D rapid prototyping technique?
For physical products, 3D printing is often favoured due to its speed, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Other methods like CNC machining, laser cutting, or rapid injection moulding might be preferred for specific materials or larger quantities. It’s essential to choose a technique aligned with the product’s complexity, desired material, and the level of detail needed in the prototype. Always consider the project’s requirements and constraints when selecting a rapid prototyping method.
How can 3D prototypes be used when designing products?
Prototypes in product design serve multiple purposes. They help validate and refine concepts, enabling designers to test functionality, ergonomics, and aesthetics. Early-stage prototypes, like sketches or mock-ups, aid in visualising ideas and gathering initial feedback. Functional prototypes test mechanical aspects and ensure the design works as intended. High-fidelity prototypes, closely resembling the final product, are used for user testing, market validation, and can support investor pitches. By iterating through prototypes, designers reduce the risk of costly mistakes in the production phase, ensuring a more efficient, user-centric, and successful product launch.
How do you create a prototype product design?
To create a prototype product design, start by defining the prototype’s purpose, such as testing functionality, user interaction, or aesthetics. Next, select a suitable prototyping method: sketches for initial ideas, digital mock-ups for visual presentation, or physical models for tangible assessment. Utilise tools like CAD software for detailed designs or 3D printers for tangible models. For software or digital products, wireframing tools can be used. Test the prototype, gather feedback, and iterate based on the results. The complexity, materials, and techniques chosen will vary depending on the prototype’s intended purpose and the product’s development stage.
Like to learn more?
Socials



