Design for manufacturing services to get your product ready for production.
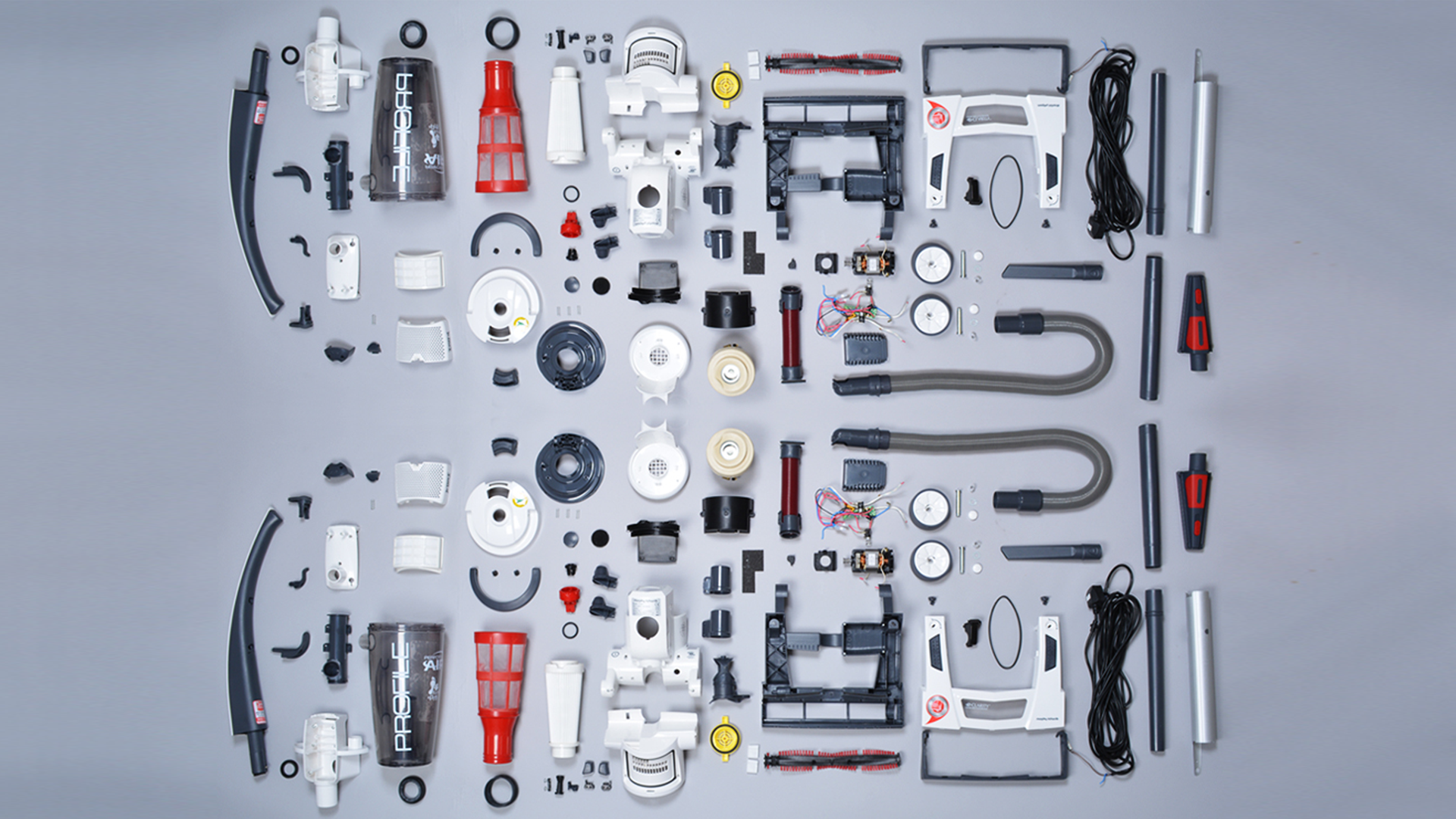
Design for manufacturing (DFM) is the process of designing a product in a way that makes it easier and less expensive to manufacture. DFM considers all aspects of the manufacturing process, from the design of the product itself to the materials and components used, and how they are assembled. By doing so, businesses can reduce painful mistakes, manufacturing costs and create a more efficient production process which delivers a better product by design.
Table of Contents
DFM is especially important for companies who produce products that are complex or contain many parts. By carefully designing their product in a way that is easy to develop, companies can save a lot of headaches and time in the long run. DFM is not a single process or technique, but rather an approach that should be adopted throughout the research and development stage to manufacture as an integral part of a company’s strategy. With everyone working together to ensure that the product can be created and optimised to suit the business’s requirements.

Choosing the right manufacturing process that suits the product and the business’s needs
Selecting the right manufacturing process is critical to the success of any product. Designers, Engineers and product design consultants must consider many factors including cost, material, quantities, surface finish, complexity and post-processing requirements when making this decision. The most appropriate manufacturing method will depend on the product, its intended use, production quantities, timescales and life cycle prior to replacement.
Therefore it is important to finalise the desired manufacturing process early in the development cycle as it has a significant impact on the design of the product. For example, high-volume consumer products that will be injection moulded need to be designed for this process from the start. This means all manufacturing requirements need to be accounted for such as draft angles, undercuts and wall sections to ensure the product is fit for purpose and cost-effective.
In the case of low volume production quantities, additive manufacturing and 3D Printing technologies alongside resin vacuum casting, thermoforming or digital fabrication may be preferable. These processes require less capital expenditure and are faster routes to production than conventional manufacturing options enabling businesses to get to market swiftly. However, this may be at the expense of higher unit cost.
In many cases, it’s often necessary to use several manufacturing processes to produce all the components that make up a product. This can be beneficial as it allows manufacturers to select the best process and material to meet the requirements of each individual part. However, using this strategy can become expensive and time-consuming, potentially more tooling and assembly, so it is important to weigh up the pros and cons before deciding on the best approach.
Finally, the overall viability of the product should be used as the deciding factor instead of just considering the manufacturing cost – does it meet all the business objectives? It is possible that a manufacturing process has a low production cost, but other factors related to it such as material availability or distribution issues may make it less viable in comparison to alternative options.
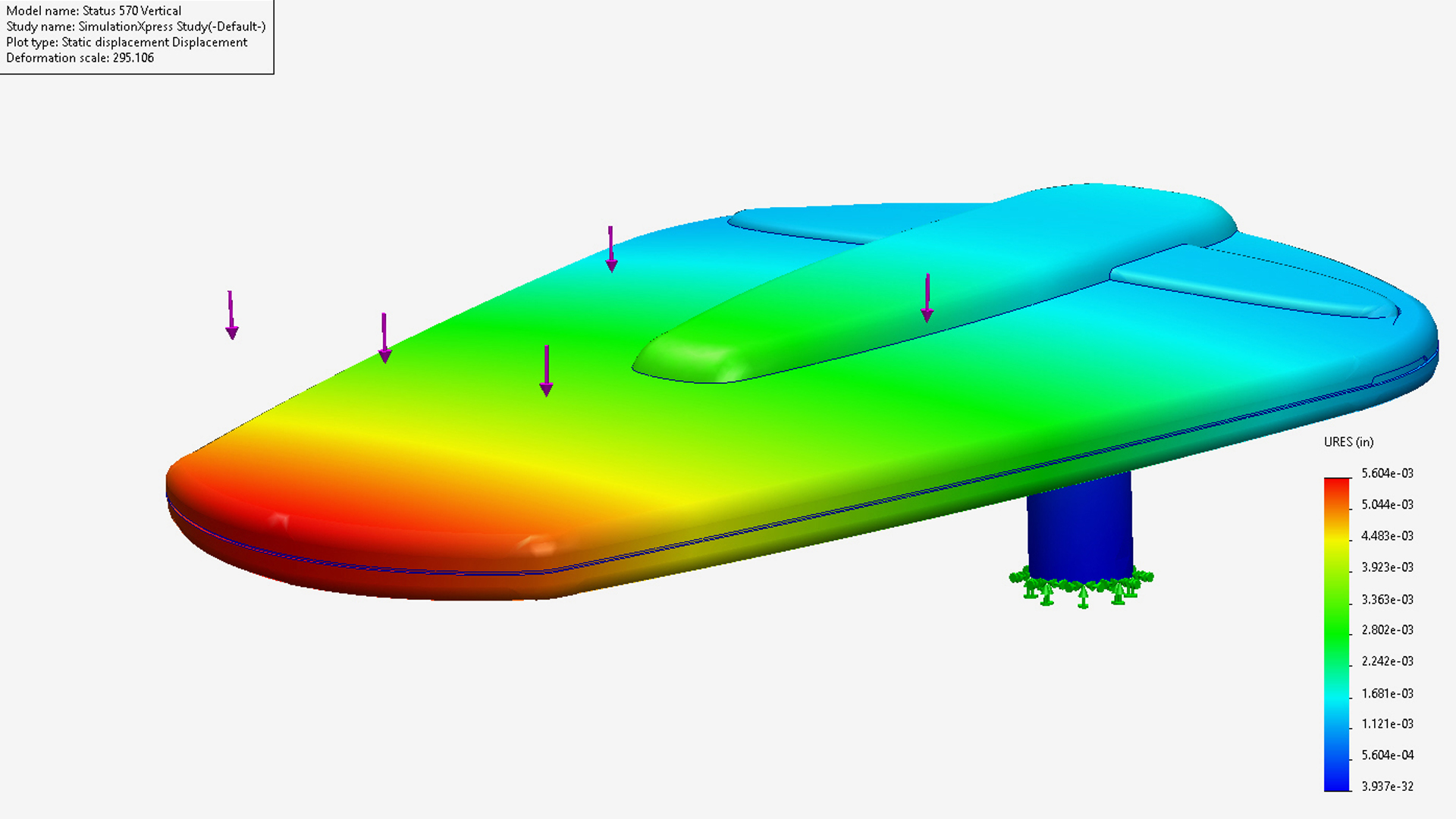
Ensuring the design is optimised for manufacture.
Design for manufacture is essential to ensure a successful outcome for production. It can be the difference between a product that is easy to manufacture and cheap to produce, to one that is difficult and costly which may fail in operation. For more demanding products, design engineers can provide computer simulations using Finite Element Analysis and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis to inform the decision-making process. For example, Mould Flow Analysis shows how a polymer will fill a mould during the injection moulding cycle to ensure the design is optimised before any tooling or parts are manufactured.
It’s beneficial to reduce material costs whenever possible. For example, when it comes to injection moulding products with thick or varying wall thicknesses, design for manufacturing shows us that it would be far better to maintain a uniform general wall section. This is understood by an experienced design engineer but may not be so clear to others. Not only will the moulding cycle be reduced saving money but material usage will be less and resources go further helping to improve sustainability.

Selecting the right materials for the product
Selecting the right materials for a product early on in the design process is an important aspect of DFM. Various factors need to be considered such as how strong the material needs to be, how well it handles stress, heat or electricity, what kind of surface finish is required, what environment is it used in and whether will it perform effectively against requirement.
Many products are constructed from several components in a variety of materials, including plastics, metals and composites. In this situation the design engineer needs to carefully think through the options, understanding how selecting one material over another may impact the feasibility of their design and the performance of the finished product.

Ensuring the product meets the required certifications and standards
One of the key aspects of DFM is making sure that the product meets all testing and compliance requirements. This can involve developing the product to address specific industry or regulatory standards, or simply ensuring that the product can be tested and pass all required certifications. Failure to do so can result in significant costs and delays in bringing the product to market. By including DFM procedures and testing the design for compliance, manufacturers can avoid these pitfalls and produce a quality product that meets these standards the first time.
The key benefits and what to consider going forward with DFM
Some key takeaways of DFM are; cost reduction, shorter time to market, improved product quality, streamlined product development, smoother manufacturing, and the ability to quickly scale up production if required.
Obviously, this is all achievable if the resulting design intent from the development process has been clearly communicated and transferred to the manufacturing phase of the project. It is essential that the design engineer provides a concise and accurate data pack, including a fully detailed requirement specification, toleranced drawings and bill of materials to ensure the end outcome meets expectations. A good design engineer will be involved throughout the duration of this process from launch of product to beyond.
It is easy to overlook DFM, but our case studies have shown that the proper application of these principles can generate successful results. Our team of experts at Product Design Consultancy are well-versed in ensuring products are suitable for manufacture and would be happy to help companies achieve their manufacturing goals.
Bluefrog Design is an award-winning Industrial Design Consultancy with over 30 years of experience. We help brands and businesses solve problems to gain a competitive advantage in the physical world. Enabling organisations to grow and launch new products that are always Better by Design. To learn about our design for manufacturing services please call on +44 0116 2530612 or email at: mail@bluefrogdesign.co.uk
About our team: https://bluefrogdesign.co.uk/about/
Design for Manufacturing Services: https://bluefrogdesign.co.uk/design-for-manufacturing/
Ready to get started on a project?
Socials



